AI Prompt Engineering Best Practices: Designing UX for AI Interfaces
Introduction
As AI-driven interfaces become mainstream, traditional UI/UX principles are being reshaped. Instead of fixed dropdowns, buttons, and forms, we now design for prompt-based interactions where users instruct AI in natural language or structured prompts.
But here’s the catch: good prompts need good UX scaffolding. Without proper UX patterns, users face ambiguity, frustration, and inconsistent AI responses.
This article is a practical guide for Designers & Developers to build intuitive AI-driven UIs that blend Laws of UX with Prompt Usability Patterns.
Why UX for Prompts is Different
| Traditional UI UX | Prompt-driven UX |
|---|---|
| Fixed UI controls (buttons, sliders, forms) | Open-ended, flexible input (prompts) |
| Users choose from predefined actions | Users craft instructions to get desired output |
| Error prevention via input constraints | Errors depend on prompt clarity & context |
| Predictable system responses | AI outputs can vary across contexts |
Core UX Laws Adapted for Prompt Interfaces
1. Jakob’s Law (Familiarity Bias)
Users prefer interfaces that feel familiar to them.
Prompt UX Pattern:
Provide Prompt Templates & Examples resembling familiar tasks.
Example:
For an AI writing assistant:
“Summarize this article in bullet points”
“Rewrite this paragraph in a friendly tone”
Design Tip:
Use placeholder text & sample prompts to lower cognitive load.
2. Hick’s Law (Choice Overload)
The more choices, the longer it takes to decide.
Prompt UX Pattern:
Offer Preset Quick Actions for common prompts, alongside a custom input field.
| Quick Actions | Custom Prompt Field |
|---|---|
| Summarize Text | <input placeholder="Custom Instruction..."> |
| Generate Image Description | |
| Fix Grammar |
3. Fitts’s Law (Touch Targets)
The time to acquire a target is a function of its size and distance.
Prompt UX Pattern:
Make the Prompt Assist Controls (like prompt suggestions, variables) easily tappable and within reach.
4. Aesthetic-Usability Effect
Users perceive aesthetically pleasing designs as more usable.
Prompt UX Pattern:
Design clean, minimal prompt interfaces with progressive disclosure (show advanced prompt options only when needed).
| Basic Mode | Advanced Mode (Expandable) |
|---|---|
| Simple prompt input + action button | Variables, Temperature, Tone selectors |
5. Tesler’s Law (Law of Conservation of Complexity)
Every system has a certain amount of complexity that cannot be reduced.
Prompt UX Pattern:
Simplify common prompts but allow advanced users to fine-tune complex ones via Prompt Parameter Controls.
Best Practices for Prompt UX Design
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| ✅ Use placeholders & example prompts to guide users | ❌ Don’t assume users know how to craft effective prompts |
| ✅ Offer quick-action buttons for common use-cases | ❌ Don’t overwhelm with too many prompt customization options upfront |
| ✅ Provide real-time AI output previews | ❌ Don’t hide AI errors/failures from users |
| ✅ Use context-aware prompt suggestions | ❌ Avoid static, one-size-fits-all prompt templates |
Sample Prompt Input UI Design (HTML + Tailwind CSS)
Error Handling & Feedback UX
| Scenario | UX Feedback Pattern |
|---|---|
| Ambiguous Prompt | Inline hint: “Your instruction is too vague. Try adding more details.” |
| AI Model Error/Timeout | Non-intrusive toast notification + Retry button |
| Unexpected AI Output | “Was this result helpful?” feedback UI |
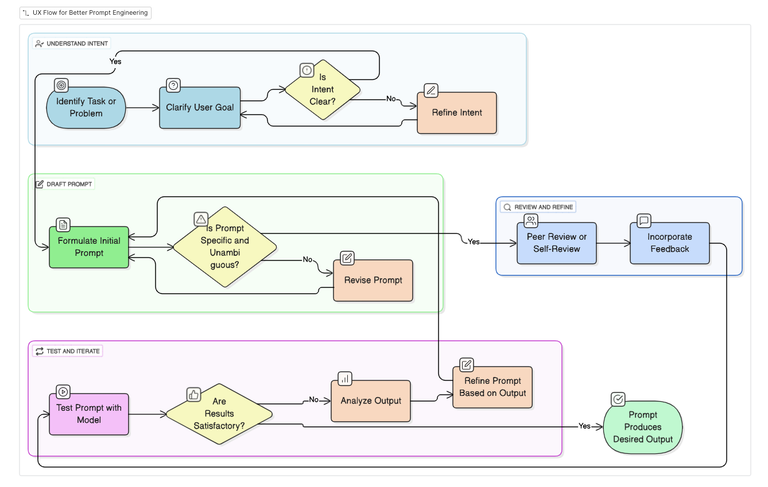
Visual Illustration: Prompt UX Flow
Prompt UX Pattern Library (Cheat Sheet)
| Pattern Name | Description | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt Templates | Predefined task instructions | “Summarize this article in 5 bullet points” |
| Prompt Autofill | Predicts & auto-completes prompts | Auto-complete after typing “Generate a...” |
| Contextual Prompt Hints | Dynamic suggestions based on content | “You’ve selected a paragraph. Rewrite it?” |
| Prompt Variables | Insert dynamic placeholders in prompt | “Write a product description for [ProductName]” |
| Tone & Style Modifiers | UX controls for adjusting tone, length, creativity | Sliders, dropdowns, and toggles |
| Result Feedback Loop | Thumbs up/down, “Improve Result” options | Inline feedback after output generation |
Advanced Patterns for Power Users
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Prompt Chaining UI | Allows users to stack multiple prompts in sequence |
| History & Reusable Prompts | Save and reuse frequently used prompts |
| Parameter Fine-tuning Panel | Adjust AI model parameters visually |
| Prompt Test Playground | Live testing of different prompt variations |
Conclusion
Designing UX for AI prompt interfaces isn’t about reinventing UX laws but reinterpreting them for human-AI collaboration. By embedding familiar design patterns, simplifying prompt crafting, and providing transparent feedback loops, we can empower users to harness AI effectively—without feeling like prompt engineers.
Good prompt UX ≠ Blank text box + Run button.
It’s a guided experience where users feel in control while AI does the heavy lifting.
Next Steps:
Create a Prompt UI Component Library (React/Vue) for reusability.
Run Usability Testing Sessions to validate prompt usability patterns.
Document a Prompt UX Pattern Playbook for your team.


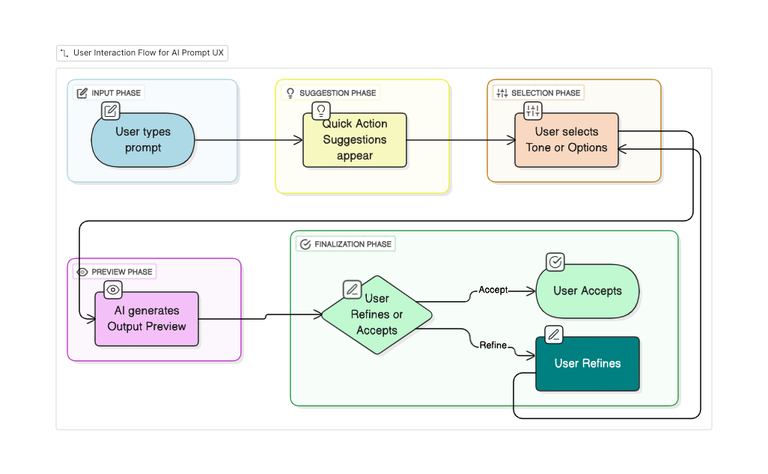






Comments